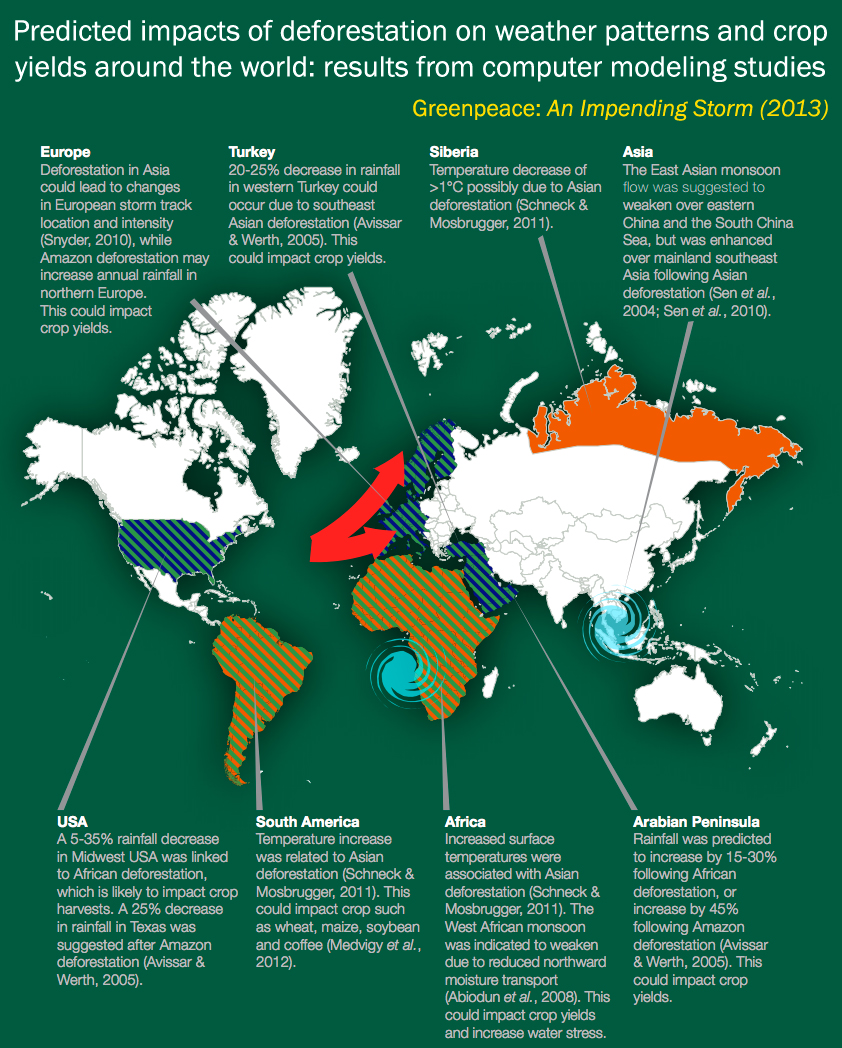
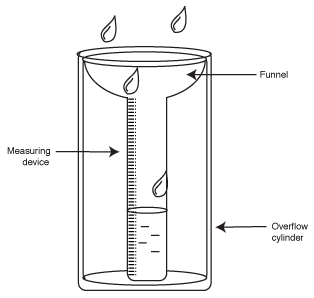
Weather elements and the instruments to collect them
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Precipitation
- Pressure
- Wind
1. Temperature: Maximum-minimum thermometer
Source: http://www.walterproducts.com/products-main/measurement/temperature/thermometers/maximum-minimum-thermometer
https://golearngeo.wordpress.com/category/formula/
2. Humidity: Wet-and-dry bulb thermometer (hygrometer)
Source: http://www.psscientific.com/shop/humidity/analog-hygrometers/reedmodelwd-5wetdrybulbhygrometer.aspx
http://weatherweatherweather.blogspot.com.br/p/all-about-weather.html
3. Precipitation: Rain gauge
Source: http://www.theolivecentre.com/Olive-Equipment/Weather-Monitoring/Rain-Gauge.html
http://www.factmonster.com/cig/weather/measuring-rain.html
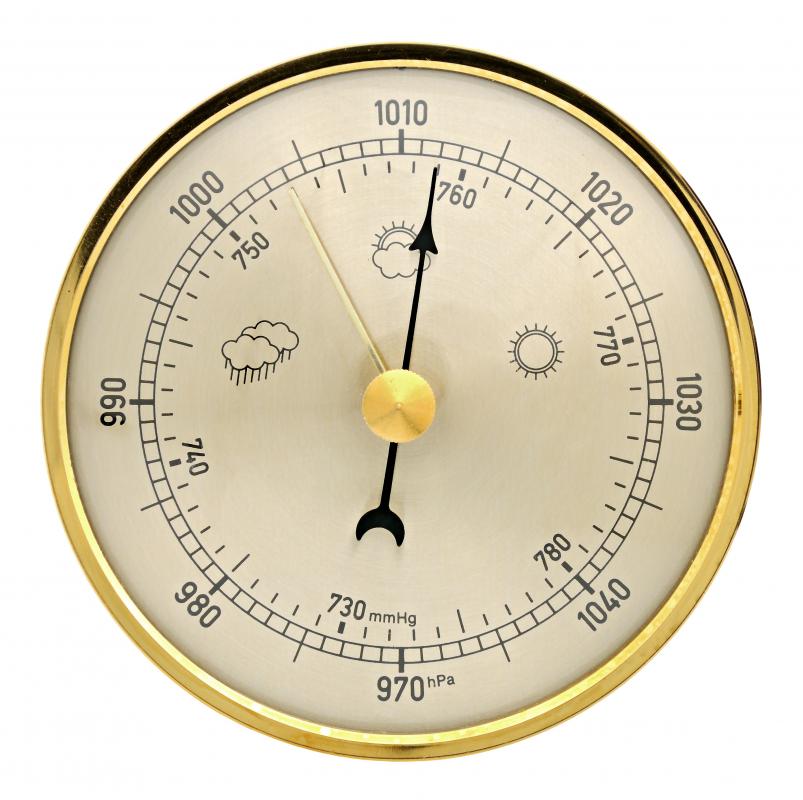
4. Pressure: Barometer
Source: http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-a-barometer.htm
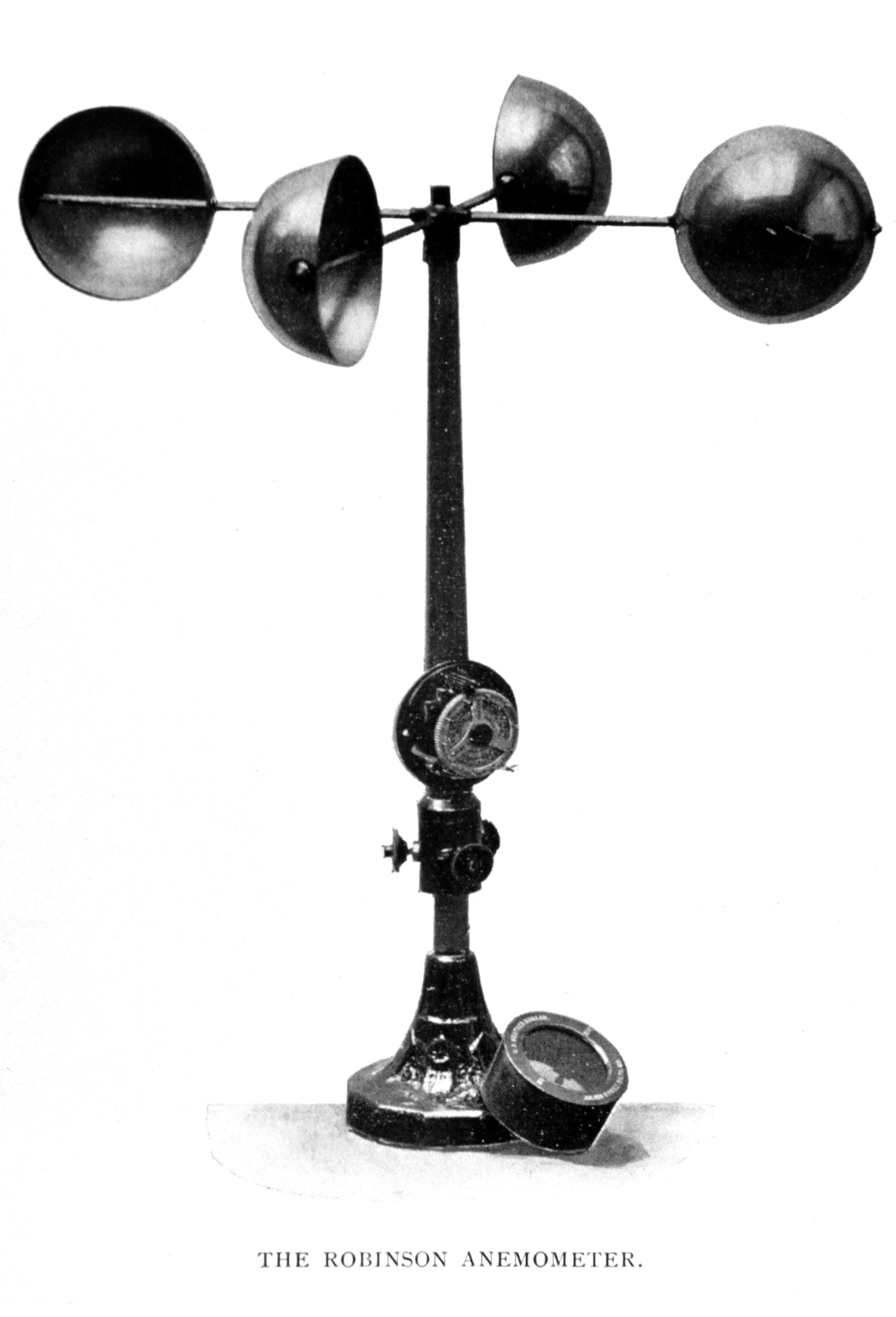
5. Wind: Anemometer and wind vane
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anemometer
http://www.testolimited.com/testo-417-vane-anemometer
Source: http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-a-wind-vane.htm
Some other instruments
Sunshine recorder
Source: http://www.kuriositas.com/2011/02/campbellstokes-sunshine-recorder.html
http://www.econet.org.uk/weather/sun.html
Stevenson screen
Source: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/cdo/images/about/stevenson.jpg
The Stevenson Screen or thermometer screen is a standard shelter (from rain, snow and high winds, but also leaves and animals) for meteorological instruments, particularly wet and dry bulb thermometers used to record humidity and air temperature.
It is kept 1.25m/4.1ft (UK standard) above the ground by legs to avoid strong temperature gradients at ground level, has louvred sides to encourage the free passage of air, and is painted white to reflect heat radiation, since what is measured is the temperature of the air in the shade, not of the sunshine.
Source: http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/wxfacts/The-Stevenson-Screen.htm
Measuring cloud cover
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Okta
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/geography/physical_processes/weather_climate/revision/3/
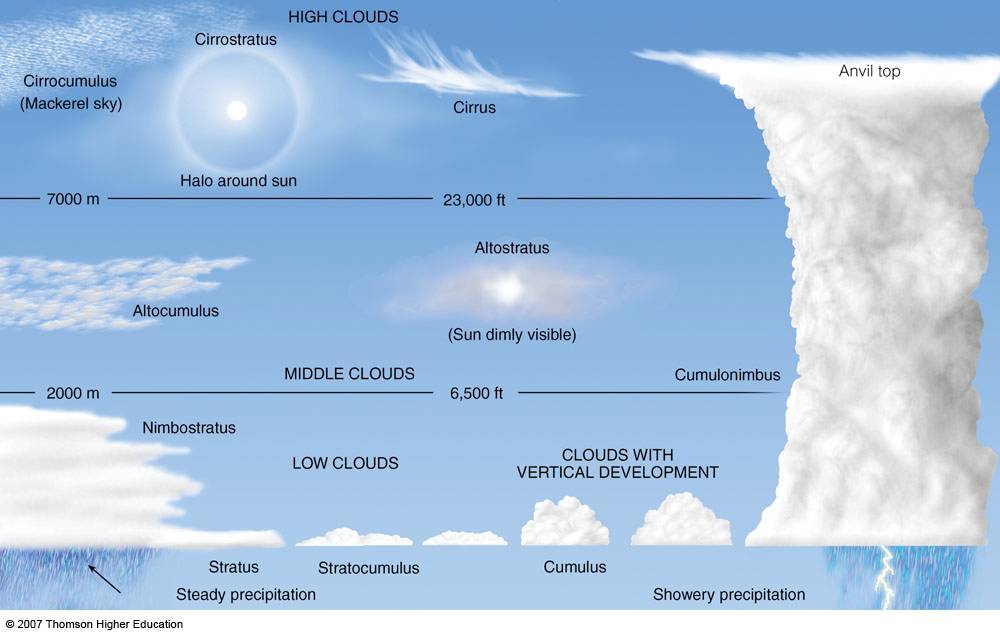
Types of clouds
Source: http://www.chemtrailplanet.com/CloudTypes.jpg
High clouds (6000 to 13000m)
Cirrus - Ci
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Cirrocumulus - Cc
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Cirrostratus - Cs
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Middle clouds (2000 to 6000m)
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Altocumulus - Ac
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Low clouds (0 to 2000m)
Nimbostratus - Ns
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Stratocumulus - Sc
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Stratus - St
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Cumulus - Cu
Cumulus clouds are ranked by their size, they are all pre stages to a cumulonimbus. A cumulus fractus is a "piece of a cumulus cloud.
CUMULUS FRACTUS < CUMULUS HUMILIS < CUMULUS MEDIOCRIS < CUMULUS CONGESTUS < CUMULONIMBUS
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ
Cumulonimbus - Cb
Picture by Luís Carlos Torelli - UMAPAZ