The rapid increase in the world's population
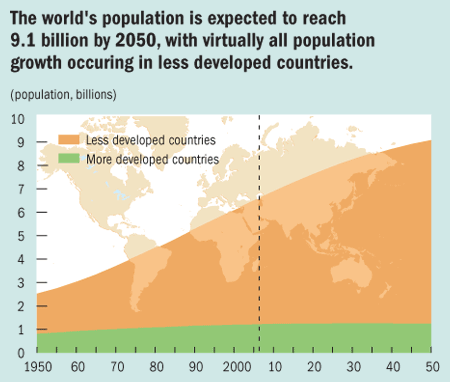
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2006/09/picture.htm

Source: http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/intermediate2/geography/human_environments/world_population_change/revision/1/
Reasons for the rapid increase in the world's population (from Bitesize):
The reasons for this rapid expansion in growth are mainly due to a rapid decrease in global death rates whilst birth rates remained very high. This meant that many more people were being born than were dying so the population grew. This difference between birth rates and death rates is called the natural increase.
In developed countries birth rates and death rates both used to be high but with advances in modern medicine, improvements in water and sanitation as well as a better diet, lead to a decrease in death rates. There was a decrease in birth rates also as the status of women improved, contraception became more readily available, careers became more important, the cost of raising a family increased and people married later. The population in the developed world is therefore fairly stable and neither rising nor falling significantly.
In developing countries death rates have also decreased rapidly but birth rates have remained extremely high due to the need for children to go out and work to bring in income for the family to look after parents in old age. This is due to a lack of pensions and due to the lack of availability and knowledge of contraception and family planning. As birth rates are so much higher than death rates there is rapid population growth in developing countries.
Source:http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/intermediate2/geography/human_environments/world_population_change/revision/1/
Causes of change in population size
The size of a country's population is influenced by three factors:
- Birth rate (fertility)
- Death rate (mortality)
- Migration
Natural population growth is calculated by subtracting a country's death rate out of its birth rate.
Net migration is calculated by subtracting a country's number of emigrants out of its immigrants.

Source: http://www.prb.org/Publications/Lesson-Plans/HumanPopulation/FutureGrowth.aspx
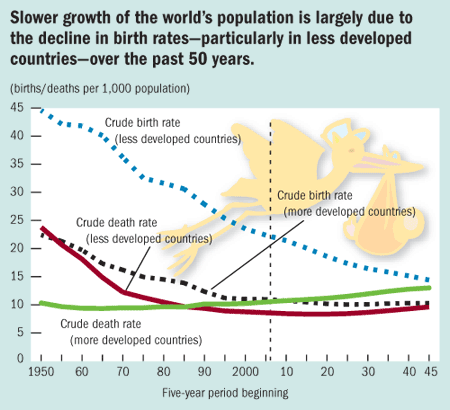
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2006/09/picture.htm
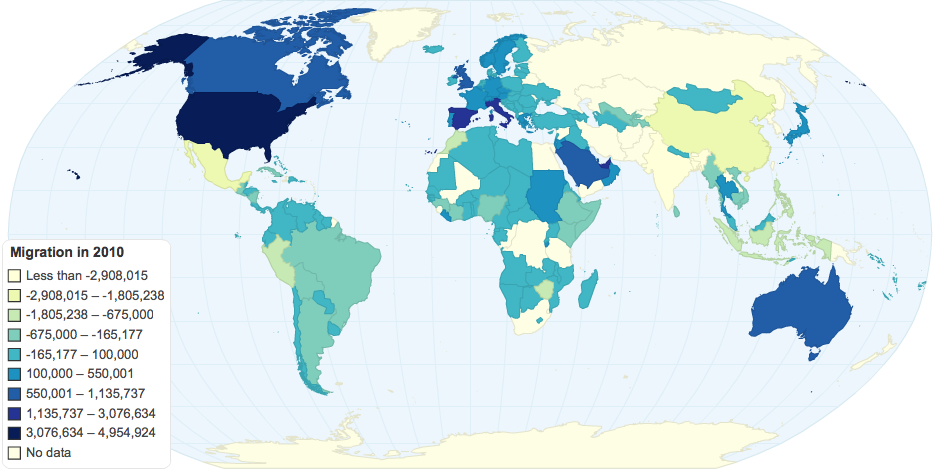
Source: http://chartsbin.com/graph?search_q=net%20migration%20rate

No comments:
Post a Comment