Population density
To determine an area's population density, you just have to divide an area's total population by the land area in square miles (or square kilometers).
Source: http://geography.about.com/od/populationgeography/a/popdensity.htm
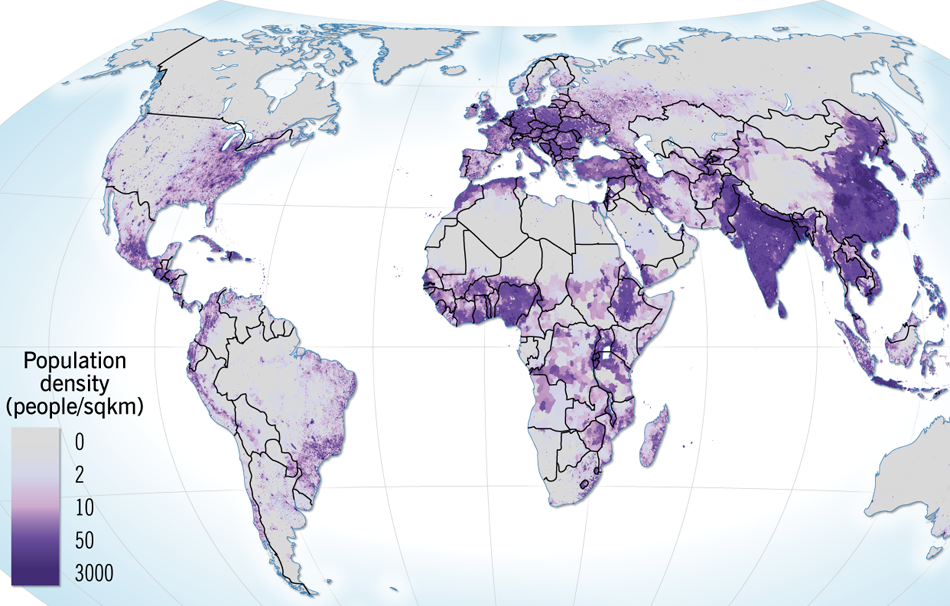
Source: https://nordpil.com/portfolio/mapsgraphics/population-density/
Factors influencing the density and distribution of population
Physical Factors
|
High Density
|
Low Density
|
| Relief (shape and height of land) | Low land which is flat e.g. Ganges Valley in India | High land that is mountainous e.g. Himalayas |
| Resources | Areas rich in resources (e.g. coal, oil, wood, fishing etc.) tend to densely populated e.g. Western Europe | Areas with few resources tend to be sparsely populated e.g. The Sahel |
| Climate | Areas with temperate climates tend to be densely populated as there is enough rain and heat to grow crops e.g. UK | Areas with extreme climates of hot and cold tend to be sparsely populated e.g. the Sahara Desert |
Human Factors
|
High Density
|
Low Density
|
| Political | Countries with stable governments tend to have a high population density e.g. Singapore | Unstable countries tend to have lower population densities as people migrate e.g. Afghanistan. |
| Social | Groups of people want to live close to each other for security e.g. USA | Other groups of people prefer to be isolated e.g. Scandinavians |
| Economic | Good job opportunities encourage high population densities, particularly in large cities in MEDCs and LEDCs around the world. | Limited job opportunities cause some areas to be sparsely populated e.g. Amazon Rainforest |

No comments:
Post a Comment